A DNS TXT record is used to associate arbitrary text with a given domain. Often, it is used to validate that a given domain is who they claim to be. For example, when signing up for google services, and you want to configure google to trust your authentication provider, they may give you a TXT record to add to your domain and for which they can check.
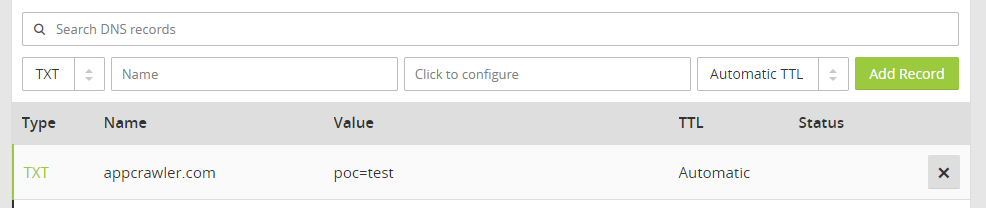
Shortly thereafter, you should be able to dig your new TXT record…
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-11-182 ~]$ dig -t txt appcrawler.com ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.62.rc1.56.amzn1 <<>> -t txt appcrawler.com ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 62761 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;appcrawler.com. IN TXT ;; ANSWER SECTION: appcrawler.com. 60 IN TXT "poc=test" ;; Query time: 72 msec ;; SERVER: 172.31.0.2#53(172.31.0.2) ;; WHEN: Wed Feb 7 17:51:28 2018 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 53 [ec2-user@ip-172-31-11-182 ~]$